Verification Case 02: Crown Fire
Torching occurs when a surface fire ignites ladder fuels or the canopy base, in turn carrying fire to the upper parts of the tree canopy. Physically, torching does not occur if flames from surface fuels are not sufficiently intense to ignite ladder fuels and/or the canopy base. Therefore, simple physical arguments suggest that crown fire initiation is a function of canopy base height, fuel moisture content (since it affects ignitability), and a measure of surface fire intensity such as flame length or fireline intensity (heat release rate per unit length of fireline).
The most widely used correlation for crown fire initiation is a go/no-go test based on fireline intensity. Crown fire occurs only when fireline intensity exceeds a critical value (\({\dot{Q}}_{\text{crit}}^{'}\)), otherwise, surface fire occurs. \({\dot{Q}}_{\text{crit}}^{'}\) for torching is estimated as [Van Wagner 1977]:
Where CBH is canopy base height (m) and \(M_{fol}\) is foliar moisture content (%). If fireline intensity of the surface fire exceeds \({\dot{Q}}_{\text{crit}}^{'}\) then either passive or active crown fire may occur.
Cruz et al. (2005) formulated an empirical model to estimate active crown fire spread rate from 10 m wind speed (u10, km/h), 1-hour fuel moisture content (M1, %), and canopy bulk density (CBD, kg/m3):
where CROSA is the crown fire rate of active spread (m/min). Active crown fire occurs only when the Criterion for Active Crowning (CAC), defined in Equation YY, is >= 1.
where R0 is the spread rate (m/min) from Van Wagner (1977) that is associated with the crown fire “lower flammability limit” - essentially a minimum mass flux of vegetation through a coordinate system attached to the flame front that permits continuous flaming:
If CAC >= 1 then active crown fire occurs with a spread rate calculated from the equation above. If CAC < 1 then passive crown fire occurs at rate CROSP:
With the theoretical bases for crown fire spread rate modeling summarized above, idealized exact solution elliptical perimeters (see Validation 01) are compared to modeled perimeters for an active crown fire test case for the following inputs:
20-ft wind speed: 12 mph
1-hr dead fuel moisture: 4%
Canopy bulk density: 0.18 kg/m3
First, 20-ft wind speed in mph is converted to 10 m wind speed in km/h:
Next, CROSA is calculated as:
Due to this rapid spread rate, L/W will be limited by the parameter
MAX_LOW as specified in the &SIMULATOR namelist group which defaults
to 8.0.
This verification test case can be run as follows:
cd $ELMFIRE_BASE_DIR/verification/02-crown-fire
./01-build-ellipse.sh
As shown in the Figure below, plotting the exact solution isochrone from
./exact_ellipses/ellipse_1.shp against the analogous isochrone generated
by ELMFIRE (./outputs/hourly_isochrones.shp) shows that the modeled
ellipse matches the exact solution.
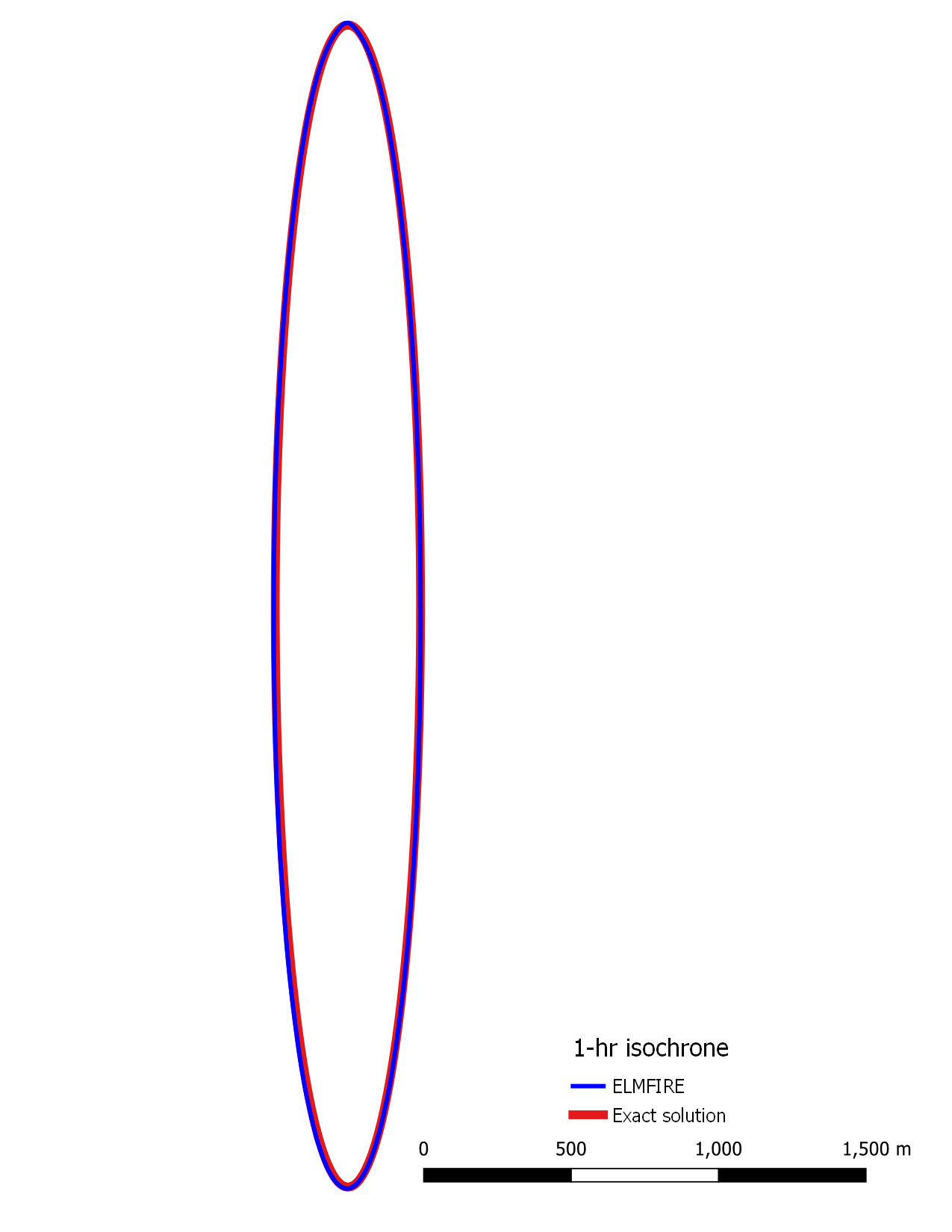
This test case verifies that:
The crown fire spread rate algorithm has been correctly implemented, and
The linkage between crown fire and surface fire (which, as described in the Technical Reference, is executed through the Rothermel model’s phi_w coefficient ) is correctly implemented